Managing the Cost of Google Cloud Servers

In the contemporary digital landscape, businesses and developers are increasingly relying on cloud service providers to drive their applications, websites, and services. Google Cloud, distinguished by its robust infrastructure and extensive service offerings, stands out prominently among cloud providers.
As organizations harness the potential of GCP services, comprehending its pricing models becomes imperative for optimizing costs and attaining value from Google Cloud.
Let’s explore the intricacies of Google Cloud pricing, highlighting key factors, considerations, and strategies for cost-effective utilization.
Jump To...
Examining Google Cloud Platform's Power and Potential
Google Cloud is a comprehensive computing platform that provides a range of cloud computing services for the development, deployment, and management of applications and services in the cloud. Computing, cloud storage, databases, machine learning, analytics, networking, and other areas are all included in its offerings.
Businesses, developers, and organisations can use Google Cloud Platform to use the company’s strong infrastructure, which enables them to create and manage online applications with increased scalability, dependability, and performance.
Important attributes and elements of the Google Cloud Platform (GCP)

Compute Services: Kubernetes Engine is used for container orchestration, Google App Engine is used for platform-as-a-service (PaaS) application deployment, and Google Compute Engine Instances is used by Google Cloud Platform to provide virtual machines (VMs).
The type of virtual machine instance (standard, high-memory, high-CPU), the deployment region, and the length of usage are some of the elements that affect virtual machine pricing.
Storage Services: Firestore and Datastore for NoSQL databases, standard storage for object storage, cloud SQL server storage for managed relational databases, and Bigtable for large-scale, low-latency data storage are just a few of the several storage solutions that Google Cloud Platform offers.
Storage capacity, storage type (e.g., local SSDs, standard storage), and storage usage patterns are some of the elements that affect cloud storage price.

Networking: Google Cloud Platform offers networking solutions such as Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) for creating private networks, Load Balancing for distributing incoming traffic, and Cloud CDN for content delivery. Network egress and ingress play a role in determining expenses, particularly for data transfer between virtual machines and external entities.
Big Data and Analytics: Google Cloud offers a range of services for processing data, including as Dataflow for batch and stream processing, BigQuery for large-scale dataset analysis, and Dataproc for managed Apache Spark and Hadoop clusters.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Google Cloud Platform provides tools for AI and machine learning, such as AI Platform for model development and deployment, Vision AI and Natural Language AI for language and image analysis, and AutoML for building personalised learning models.
Developer Tools: Google Cloud Platform provides tools for application development and deployment, including functions for serverless computing, source repositories for version control, and Cloud Build for continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD).
Security and Identity Management: Google Cloud Platform includes tools for encryption and key management in addition to security capabilities like Identity and Access Management (IAM) for limiting resource access.
Extra Services: Managed databases, load balancers, and container orchestration are all included in the Google Cloud services. If you use these services, there can be extra costs.
Recognising the Pricing Structure of Google Cloud

The Google Cloud pricing model is designed to provide flexibility and scalability, allowing users to pay for the resources they use, including compute engine instances. The pay-as-you-go concept, which lets users be billed only for the services they use and has no monthly commitment or early termination costs, is the foundation of this business model.
GCP’s pricing is influenced by various components, each contributing to the overall pricing profile:
How to Navigate Google Cloud Pricing
Google Cloud stands out with its unique and transparent pricing approach, emphasizing innovation to empower customers in controlling their spending and maximizing the value of their investment.
Revealing the Unique Price Structure
Launch Workloads at Free
Getting started with Google Cloud is both accessible and risk-free. New customers receive a generous offer of $300 in free credits, enabling them to run, test, and deploy workloads without financial constraints.
The platform offers free access to over 20 products, within specified monthly usage limits. This allows customers to explore and evaluate the platform’s capabilities before committing to any financial investment.
Just Pay for the Services You Use
Google Cloud’s pay-as-you-go pricing model guarantees that users pay only for the resources and services they consume, without any upfront fees or termination charges. The pricing models are tailored to resource usage, allowing alignment with the organization’s specific needs. This flexibility establishes an agile and cost-effective framework for innovation.

Unlock Up to 57% in Savings
Cost savings are an integral part of Google Cloud’s design, providing automatic savings based on monthly usage and discounted rates for pre-paid resources. This approach ensures substantial cost reductions for users.
Notably, users can achieve savings of up to 57% through committed use discounts on resources like machine types and GPUs.
Keep Your Expenses Under Control
Google Cloud provides users with a comprehensive suite of tools to effectively manage and optimize their spending. Users can exercise control over their budget by receiving alerts and setting quota limits to prevent unexpected expenses.
The intelligent recommendations enabled by AI on the platform provide practical insights for cost optimisation. Customers may clearly see their spending with the use of custom dashboards that show cost trends and forecasts.
Experience Google Cloud Trial Offer
The Google Cloud Free Programme offers a variety of options for customers who are new to Google Cloud services or for seasoned users who want to try something different. This programme takes the form of three different programmes, each tailored to meet the various requirements and goals of its participants.

90-Day, 300 Free Trial: An Unlimited Array of Opportunities
Those who are new to Google Cloud or the Google Maps Platform can take advantage of the 90-day, 300 Free Tier. For a generous 90 days, this alluring offer gives users an unrestricted experience within its environment.
With 300 worth of Cloud Billing credits included, users are able to investigate and assess a range of GCP services and products.
T2A Limited-Time Free Trial: An Overview of the Future
Innovation has no boundaries, and Google Cloud recognises the need of keeping on the cutting edge. The Limited Time T2A Free Trial provides users with an exclusive opportunity that promises a sneak peek into the future of cloud computing.
Free Tier: An Overview of Smooth Cloud Using
The Google Cloud Free Program isn’t just for newcomers. Even seasoned users can tap into the Free Tier, where selected products await their command, free of charge. BigQuery, storage, and compute engine are free to use up to predetermined monthly consumption caps.
Google Maps Platform Monthly Credit: Charting New Territories
Maps serve as the universal language of exploration, and the Google Maps Platform offers a recurring monthly credit of 200. This credit pays homage to both the cartographers of old and the digital explorers of today, and it is applicable to every Maps-related Cloud Billing account.
Handling Cost Estimates with the GCP Pricing Tool
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is dedicated to giving customers a thorough grasp of pricing dynamics. At the heart of this commitment lies the GCP pricing calculator, a powerful web-based tool meticulously designed to unveil the intricacies of Google Cloud’s pricing framework.
Let us now quickly review the features of the GCP pricing calculator.
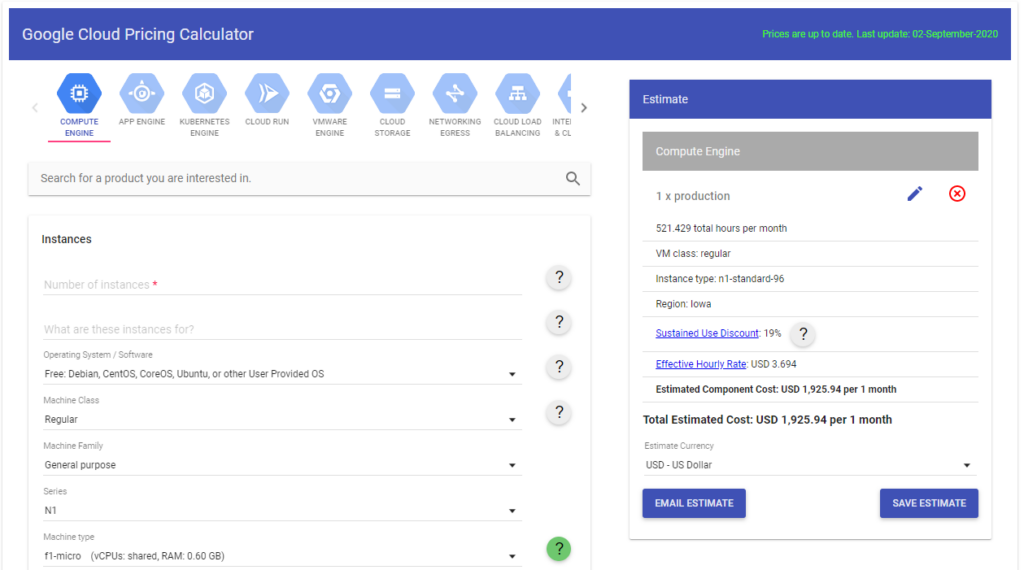
Google Cloud Pricing Calculator: A Simplified Look at Complexity
GCP’s pricing calculator is a user-friendly web interface engineered to simplify the financial aspects of cloud services. Its main goal is to provide customers with a clear visualisation of the anticipated consumption of different GCP services and resources, regardless of their level of experience with cloud computing.
The GCP pricing calculator will help you expedite your cost estimation process in the following ways:
Instantaneous insights and configuration input
To optimize calculator functionality, it is crucial to input specific details regarding the setup, including instance type, regions for data operations, and anticipated data usage. By providing these particulars, the calculator can swiftly generate a real-time estimate of associated expenses.
This capability empowers users to anticipate and plan for the financial aspects of their cloud endeavors. It enables proactive decision-making aligned with individual pricing considerations.
Recognizing the varied requirements of its users, the GCP calculator offers flexibility in adjusting essential variables. Users can tailor currency and time-frame settings to their specific needs, ensuring that estimated expenses are presented in a manner that aligns with their financial context.
Recognising Cloud Billing
At its essence, Cloud Billing constitutes a comprehensive suite of tools that provides a holistic solution for overseeing Google Cloud expenses. These GCP services enable customers to do more than just pay their bills; they also enable them to analyse their spending habits, make wise decisions, and streamline their financial operations.
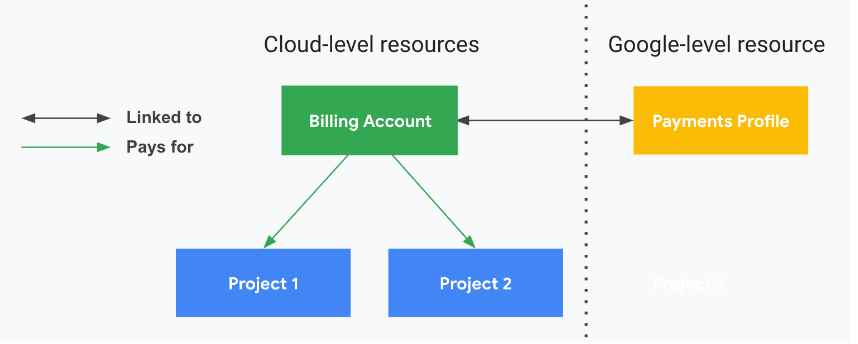
The cornerstone of Cloud Billing is the creation of a Cloud Billing account within the Google Cloud ecosystem.

The Cloud Billing Account's Critical Role
Centralized Management: The Cloud Billing account functions as a centralized hub at the cloud level, efficiently administered within the Google Cloud console. It serves as the hub, bringing together all financial operations from various initiatives.
Responsibility Assignment: This account plays an important part in assigning costs to specific individuals or teams, clearly delineating the financial responsibility for a particular set of Google Cloud resources and services, including Google Maps Platform APIs.
Access Management: Using IAM roles, access to a Cloud Billing account is carefully controlled so that only authorised workers are able to explore and handle billing-related tasks.
Integrated Payments: A Google payments profile, which contains crucial payment details including the payment method used to settle bills, is easily integrated with a Cloud Billing account.
Detailed Cost Tracking: It acts as a robust tracker, meticulously documenting all incurred expenses, including charges and usage credits, across all projects connected to the Cloud Billing account.
Consolidated Invoicing: One major benefit is that it simplifies the financial overview by creating a single, consolidated invoice for each Cloud Billing account.
Single Currency Operation: By operating in a single currency, cloud billing streamlines cost control and makes cross-border transactions easier.
The Function of Google Payments Profile
Global Payment Nexus: The Google payments profile expands its reach beyond Cloud Billing, seamlessly connecting you to a range of Google services, from Google Ads to Fi phone service.
Comprehensive Payment Processing: It goes beyond Google Cloud, handling payments for different Google services and providing a consistent method for handling financial transactions.
Integrated Information Repository: Your payments profile serves as a secure repository, storing vital details such as your name, address, and, if required by law, tax ID.
Hub for Payment Instruments: It contains a range of payment options, including bank accounts, credit cards, and debit cards that are linked to your transaction history.
Streamlined Document Management: Serving as a central document center, the payments profile provides a simplified view of your financial history, including invoices and payment records.
Access and Control: You keep the power to decide who can see and receive bills for your various Cloud Billing accounts and related products.
Varied Billing Cycles: Navigating Self-Serve and Invoiced Cloud Billing:
Self-Serve Accounts: In the event that an individual chooses to use self-serve Cloud Billing, expenses are automatically deducted via threshold-based or regular monthly billing, contingent upon a predetermined cumulative total.
Invoiced Accounts: Alternatively, invoiced Cloud Billing accounts receive a monthly invoice, and the payment terms are defined by your unique agreement with Google.
Strategies for Cost Optimisation

Cloud computing offers unmatched flexibility and scalability, but it necessitates vigilant cost management. Without proper oversight, expenses can rapidly escalate. Fortunately, Google Cloud provides strong cost control and cloud deployment value strategies and tools. Here’s a detailed roadmap to effectively optimize your cloud bill:
1. Understanding Billing and Cost Management Tools
Understanding cloud expenses is the first step towards optimisation. A number of free invoicing and expense management tools are available from Google Cloud, providing insightful data on spending trends. Sort expenses according to your company’s needs first.
- Use billing reports to get a detailed breakdown of your expenses.
- To allocate costs to particular departments or teams, apply labels, and create personalised dashboards for in-depth cost analysis.
- To avoid going over budget, keep an eye on trends, establish budgets, and set up notifications. Learn how to use these tools so that you can continue to manage your cloud spending.
2. Make Effective Use of Computer Resources
Identify and eliminate unused or underutilized resources to optimize costs:
Idle VM Identification: Employ Google Cloud’s Recommenders to pinpoint inactive VMs and persistent disks based on usage metrics. Take care while removing virtual machines (VMs) and think about making snapshots as a safety precaution.
Auto Start/Stop Virtual Machines: Arrange for virtual machines to start and stop on their own when usage trends dictate. Costs can be considerably decreased by using this proactive approach, particularly in non-production settings.
Rightsizing VMs: Regularly assess and adjust machine types to align with workload demands. Utilise the rightsizing suggestions provided by Google Cloud to allocate resources as efficiently as possible, either within the same location or across other server regions.
Utilise Preemptible VMs: Harness the cost-effectiveness of preemptible VMs for fault-tolerant workloads. These instances can be used in a variety of settings and provide significant cost savings when compared to standard instances.
3. Optimize The Cost of Cloud Storage
Effectively oversee costs for storage services by implementing these strategies:
Choosing the Right Storage Classes: Take into account the frequency of data access when selecting the best storage class. To achieve maximum cost-efficiency, use lifecycle policies to automatically modify storage classes and remove unnecessary data.
Deduplication: Reduce redundant data by using careful version control and wise storage decisions. Utilise object versioning and multi-region buckets to reduce data redundancy and optimise costs.
4. Use of Smart Data Warehouses
Effectively administer BigQuery costs while maintaining performance:
Enforce Query rules: Set query limitations to avoid unforeseen expenses, and apply corresponding rules to users and projects to uphold financial limits.
Employ Partitioning and Clustering: Partitioning tables can improve query performance and cost effectiveness. Enable the “Require partition filter” option for optimal results and leverage clustering for additional performance gains.
Switch to Batch Loading: If real-time data is not critical, transition from streaming inserts to batch loading. This shift can lead to substantial cost savings without compromising data integrity.
Flex Slots: Explore the benefits of Flex Slots to optimize query pricing based on your specific workload. This flexible method guarantees economical BigQuery processing and optimal use of available resources.
5. Streamline Network Costs and Monitoring
Enhance visibility and control over your network costs with these best practices:
Determine Network Usage: To identify high-traffic services, use Cloud Platform SKUs and Network Topology. Achieve effective resource allocation by optimising their deployment according to consumption trends.
Select Service Tiers for Networks:
You can choose between regular and premium service tiers to customise your network to meet your needs. To satisfy certain requirements, take into account the trade-off between performance and cost.
Optimise Logging: Use sampling techniques to lower log volume and filter out extraneous data to fine-tune logging settings. This guarantees that pertinent data is preserved without incurring extra expenses.
By adopting these practices and leveraging Google Cloud’s tools, users can gain detailed insights into cloud spending, eliminate inefficiencies, and optimize infrastructure for both performance and cost-effectiveness.
For more advice, take advantage of Google Cloud’s free training materials. These offer insightful analyses of optimisation tactics without requiring any up-front payments, guaranteeing effective use of Google Cloud pricing.

Frequently Asked Questions
Google Cloud encompasses a diverse set of cloud-based offerings tailored for effective application management and deployment. At its core is the Google Cloud Platform, providing users with an extensive array of resources to seamlessly create, deploy, and manage cloud-based applications.
Google Cloud’s pricing structure is subject to potential changes. Nonetheless, the platform usually follows through on its policy of alerting users well in advance of any revisions or modifications. This dedication to communication attempts to uphold openness and provide users with the chance to make the appropriate corrections in reaction to price changes.
Google Cloud employs a usage-oriented pricing model, where charges are calculated based on the hours of usage attributed to specific service categories. For example, compute instance charges are determined by the monthly hours of usage, while data storage costs align with the volume of stored data. This approach ensures that users pay for the specific resources and services they consume, providing a more granular and flexible pricing structure.
Fixed machine types come with set configurations for CPU and memory, offering simplicity in deployment.
Custom machine types, on the other hand, let you define specific combinations of CPU and memory, providing flexibility and resource optimization.



